Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is one of the important driving factors in Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. The ALK fusion mutation is presented at approximately 5% in NSCLC patients and is usually common in young, non-smokers or mildly smoked lung adenocarcinoma patients. Activation of ALK activates downstream signaling pathways, leading to tumorigenesis and survival. ALK inhibitors can effectively inhibit the activity of ALK, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. | 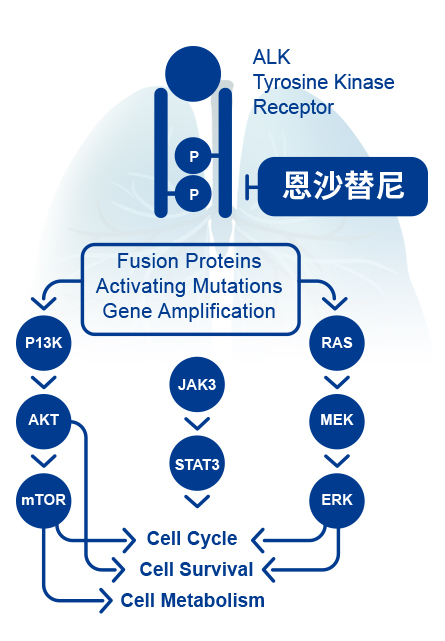 |
